25-2018-com-pres_priorities_redactedpdf
Dieses Dokument ist Teil der Anfrage „Documents on CETA: Bilateral Dialogue on Raw Materials“
[All redactions in the document have been done in line with Art.4.1(b)] Ref. Ares(2021)6044578 - 05/10/2021 EU priorities and the EU policy and regulatory environment EU-Canada Bilateral Dialogue on Raw Materials CETA Art. 25.4 1st meeting Brussels, 16 November 2018 , European Commission Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs (DG GROW) Resource Efficiency and Raw Materials Unit Raw Materials

EU Raw Materials Strategy Policy and future orientations and Commission priorities Commission priorities 2015-19 1. Jobs, Growth and Investment - circular economy and green growth 2. Digital Single Market 3. Energy Union Raw Materials Initiative - transition to a low-carbon economy EU policy (renewables, electricity market, mobility…) - CRM list 4. Internal Market EIP on Raw Materials - unlock the full potential of the single market Strategic Implementation Plan - a renewed EU Industrial Policy Strategy 6. Trade policy to harness globalisation H2020-Raw Materials - economic diplomacy - raw materials chapters in FTAs 9. A stronger global actor - international cooperation and development Raw ENTR G3 Materials

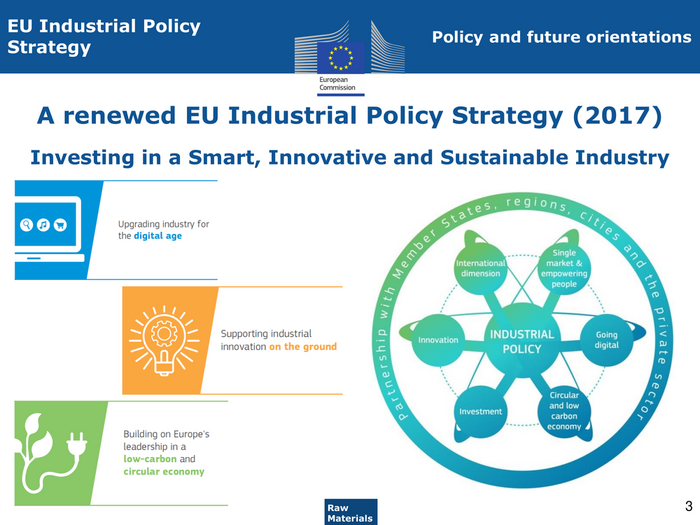
EU Industrial Policy Policy and future orientations Strategy A renewed EU Industrial Policy Strategy (2017) Investing in a Smart, Innovative and Sustainable Industry Raw 3 ENTR G3 Materials
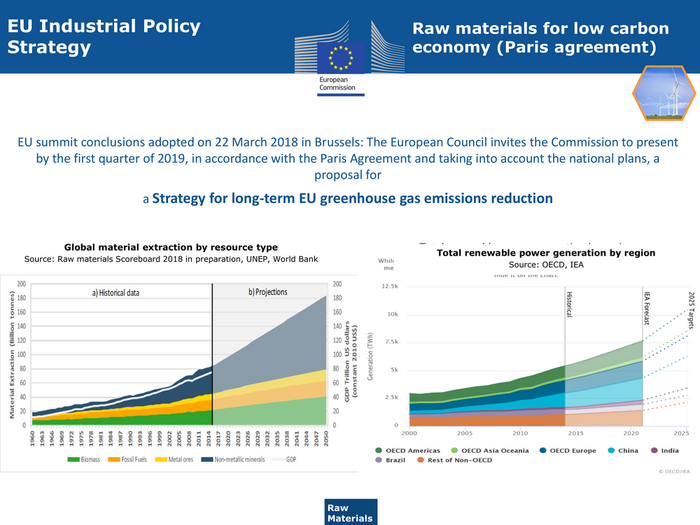
EU Industrial Policy Raw materials for low carbon Strategy economy (Paris agreement) EU summit conclusions adopted on 22 March 2018 in Brussels: The European Council invites the Commission to present by the first quarter of 2019, in accordance with the Paris Agreement and taking into account the national plans, a proposal for a Strategy for long-term EU greenhouse gas emissions reduction Global material extraction by resource type Total renewable power generation by region Source: Raw materials Scoreboard 2018 in preparation, UNEP, World Bank Source: OECD, IEA Raw Materials
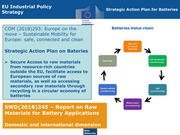
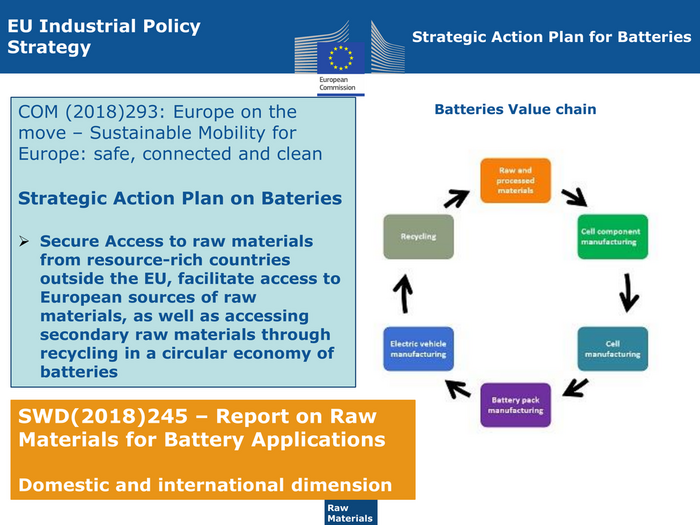
EU Industrial Policy Strategic Action Plan for Batteries Strategy COM (2018)293: Europe on the Batteries Value chain move – Sustainable Mobility for Europe: safe, connected and clean Strategic Action Plan on Bateries Secure Access to raw materials from resource-rich countries outside the EU, facilitate access to European sources of raw materials, as well as accessing secondary raw materials through recycling in a circular economy of batteries SWD(2018)245 – Report on Raw Materials for Battery Applications Domestic and international dimension Raw ENTR G3 Materials
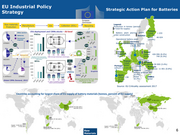
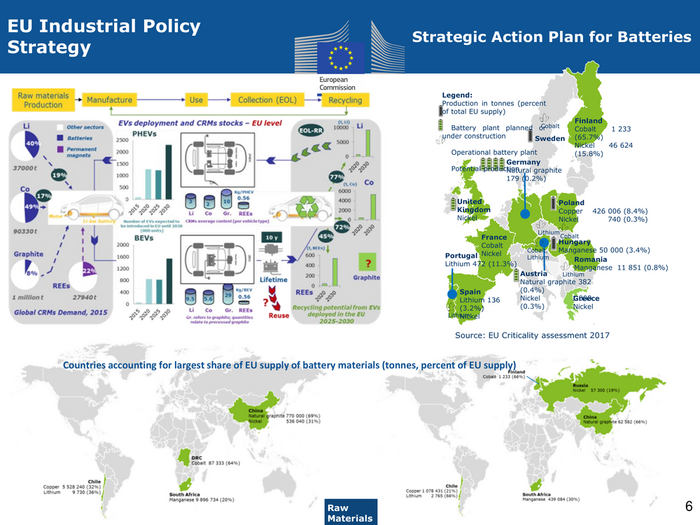
EU Industrial Policy Strategic Action Plan for Batteries Strategy Legend: Production in tonnes (percent of total EU supply) Finland Battery plant planned or Cobalt Cobalt 1 233 under construction Sweden (65.7%) Nickel 46 624 Operational battery plant (15.8%) Germany Potential production Natural graphite 179 (0.2%) United Poland Kingdom Copper 426 006 (8.4%) Nickel Nickel 740 (0.3%) Lithium France Cobalt Hungary Cobalt Cobalt, Manganese 50 000 (3.4%) Portugal Nickel Lithium Romania Lithium 472 (11.3%) Manganese 11 851 (0.8%) Austria Lithium Natural graphite 382 Spain (0.4%) Lithium 136 Nickel 1Greece 000 (3.2%) (0.3%) Nickel Lithium Nickel Source: EU Criticality assessment 2017 Countries accounting for largest share of EU supply of battery materials (tonnes, percent of EU supply) Raw 6 ENTR G3 Materials
EU Industrial Policy Energy Intensive Industries Strategy Paris agreement EIIs are the lifeblood of key value chains in EU but also their supply chains are linked to other EIIs. EIIs products are and will be needed more to enable the energy transition and will be at the forefront of low-carbon solutions. Most EIIs already see recycled materials, waste and by- products of other industries as important raw material inputs. Source: Industrial Value Chain a Bridge Towards a Carbon Neutral Europe, VUB IES, 2018 Raw Materials

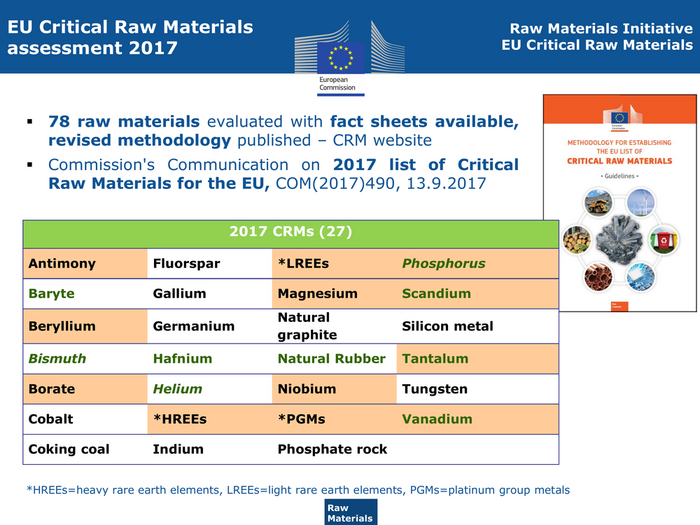
EU Critical Raw Materials Raw Materials Initiative assessment 2017 EU Critical Raw Materials 78 raw materials evaluated with fact sheets available, revised methodology published – CRM website Commission's Communication on 2017 list of Critical Raw Materials for the EU, COM(2017)490, 13.9.2017 2017 CRMs (27) Antimony Fluorspar *LREEs Phosphorus Baryte Gallium Magnesium Scandium Natural Beryllium Germanium Silicon metal graphite Bismuth Hafnium Natural Rubber Tantalum Borate Helium Niobium Tungsten Cobalt *HREEs *PGMs Vanadium Coking coal Indium Phosphate rock *HREEs=heavy rare earth elements, LREEs=light rare earth elements, PGMs=platinum group metals Raw ENTR G3 Materials
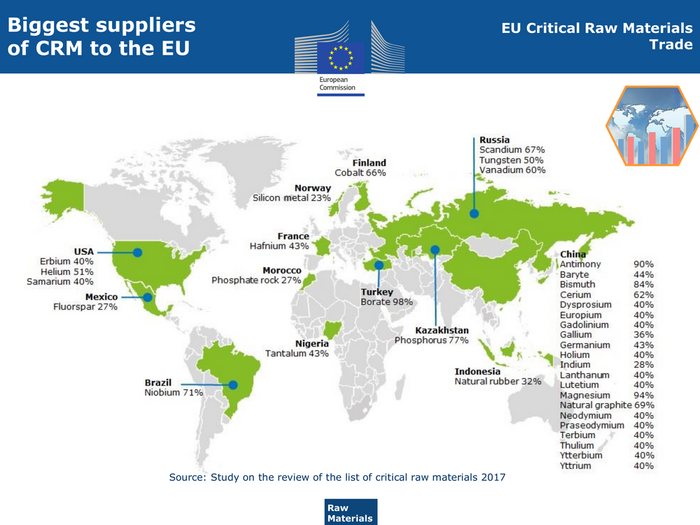
Biggest suppliers EU Critical Raw Materials of CRM to the EU Trade Source: Study on the review of the list of critical raw materials 2017 Raw ENTR G3 Materials
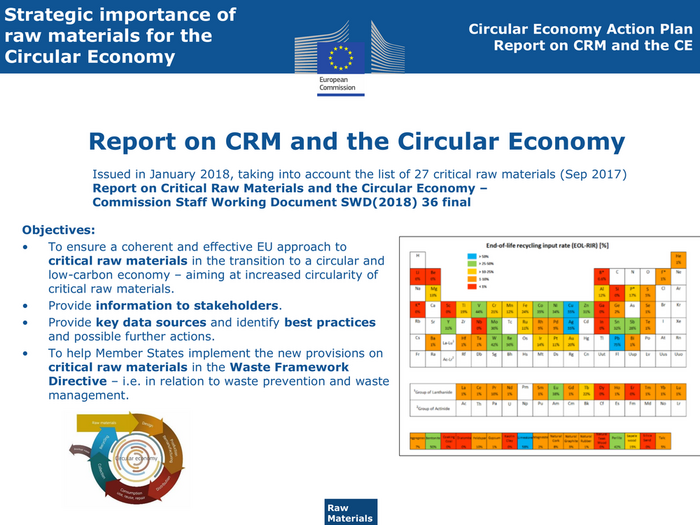
Strategic importance of Circular Economy Action Plan raw materials for the Report on CRM and the CE Circular Economy Report on CRM and the Circular Economy Issued in January 2018, taking into account the list of 27 critical raw materials (Sep 2017) Report on Critical Raw Materials and the Circular Economy – Commission Staff Working Document SWD(2018) 36 final Objectives: • To ensure a coherent and effective EU approach to critical raw materials in the transition to a circular and low-carbon economy – aiming at increased circularity of critical raw materials. • Provide information to stakeholders. • Provide key data sources and identify best practices and possible further actions. • To help Member States implement the new provisions on critical raw materials in the Waste Framework Directive – i.e. in relation to waste prevention and waste management. Raw Materials